
Introduction to the Book of the Dead

The Ancient Egyptian Book of the Dead is a complex and intriguing collection of texts that provides valuable insight into the beliefs and rituals surrounding death and the afterlife in ancient Egypt. Dating back to around 1550 BCE, this ancient funerary text was intended to guide the deceased through the perilous journey they would undertake in the afterlife and ensure their successful transition into the land of the dead.
The Book of the Dead, known by its original Egyptian name "rw nw prt m hrw" or "The Book of Coming Forth by Day," was not actually a single book but rather a compilation of spells and rituals inscribed on papyrus scrolls. These scrolls were usually buried with the deceased, as they were believed to be vital tools that would assist the souls in their journey to the afterlife.
The purpose of the Book of the Dead was to provide instructions and protection for the deceased as they navigate the treacherous underworld. It was believed that after death, the soul would undergo a series of tests and trials, with the ultimate goal of reaching the afterlife and achieving immortality. The spells and rituals within the Book of the Dead were designed to aid the deceased in overcoming these challenges and ensure their successful passage into the next life.
The contents of the Book of the Dead varied from one scroll to another, as it was a personalized text created for each individual. However, there were certain common themes and elements that appeared throughout the collection. The spells and rituals generally dealt with topics such as the protection of the deceased, the judgment of the soul, and the provision of nourishment and sustenance in the afterlife.
The Book of the Dead also included vivid illustrations and beautiful artwork, depicting scenes from the journey of the soul and the various gods and goddesses that were believed to play a role in the afterlife. These colorful illustrations not only added aesthetic appeal but also served a practical purpose, as they were thought to help guide and assist the spirit in recognizing and interacting with the divine beings they would encounter.
Despite the name "Book of the Dead," it is important to note that this collection of texts was not a religious scripture like the Bible or the Quran. Instead, it was more of a practical guidebook, providing instructions and rituals necessary for a successful transition into the afterlife. The Book of the Dead reflects the ancient Egyptians' deep fascination with death and their unwavering belief in an afterlife filled with challenges, rewards, and divine intervention.
In conclusion, the Book of the Dead serves as a fascinating window into the religious and cultural beliefs of ancient Egypt. This intricate collection of spells and rituals sheds light on the ancient Egyptians' understanding of death, their beliefs in the afterlife, and their desire for eternal existence. Through the Book of the Dead, we gain valuable insight into the intricate customs and practices surrounding death and how the ancient Egyptians sought to ensure a prosperous afterlife for their departed loved ones.
The Purpose and Use of the Book of the Dead

The Ancient Egyptian Book of the Dead held great significance in the belief system and funeral rituals of ancient Egypt. It served as a guidebook or manual for the deceased to navigate their journey into the afterlife.
A Ritualistic Guide to the Afterlife
The main purpose of the Book of the Dead was to provide the knowledge and instructions necessary for the deceased to successfully navigate the complex and perilous journey through the underworld. It was believed that the deceased would encounter various challenges and obstacles, and the Book of the Dead acted as a protective and empowering tool to overcome them.
A Roadmap for the Soul
Ancient Egyptians believed in the concept of an eternal afterlife where the soul would continue its existence. According to their belief system, the soul had to undergo a series of rituals and encounters in the afterlife to attain eternal peace and happiness. The Book of the Dead acted as a roadmap, outlining the necessary steps, spells, and rituals required for the soul to reach its final destination.
Protection and Guidance
The Book of the Dead was filled with spells and incantations intended to protect the deceased from evil forces and guide them towards a favorable judgment in the Hall of Maat, where their heart would be weighed against the feather of truth. It provided prayers, hymns, and offerings that the deceased could recite or perform to gain the favor of the gods and goddesses who held the power of judgment.
Personalized and Customized Texts
Each Book of the Dead was unique to the individual it accompanied. The text was tailored to the specific needs and desires of the deceased, taking into account their personal circumstances, profession, and status in society. The Book of the Dead would often include the deceased's name, titles, and genealogy to ensure their identity and recognition in the afterlife.
Written on Papyrus and Tomb Walls
The Book of the Dead was typically written on rolls of papyrus and sometimes inscribed on tomb walls. It was composed of several chapters, or spells, each of which had a specific purpose and function. The texts were richly illustrated with symbolic images and scenes depicting deities, mythological creatures, and ritualistic activities.
A Testament to Egyptian Beliefs and Rituals
The Book of the Dead provides us with valuable insights into the religious beliefs, cosmology, and funerary rituals of ancient Egypt. It illustrates their belief in the concept of an afterlife and the importance of proper burial and preparation for the journey beyond death. The spells and rituals contained within the Book of the Dead offer a glimpse into the mindset of the ancient Egyptians and their quest for immortality.
Overall, the Book of the Dead served as a powerful tool for the deceased to navigate the complexities of the afterlife. It provided guidance, protection, and empowerment, enabling the soul to reach its final destination and attain eternal peace and happiness.
The Content of the Book of the Dead
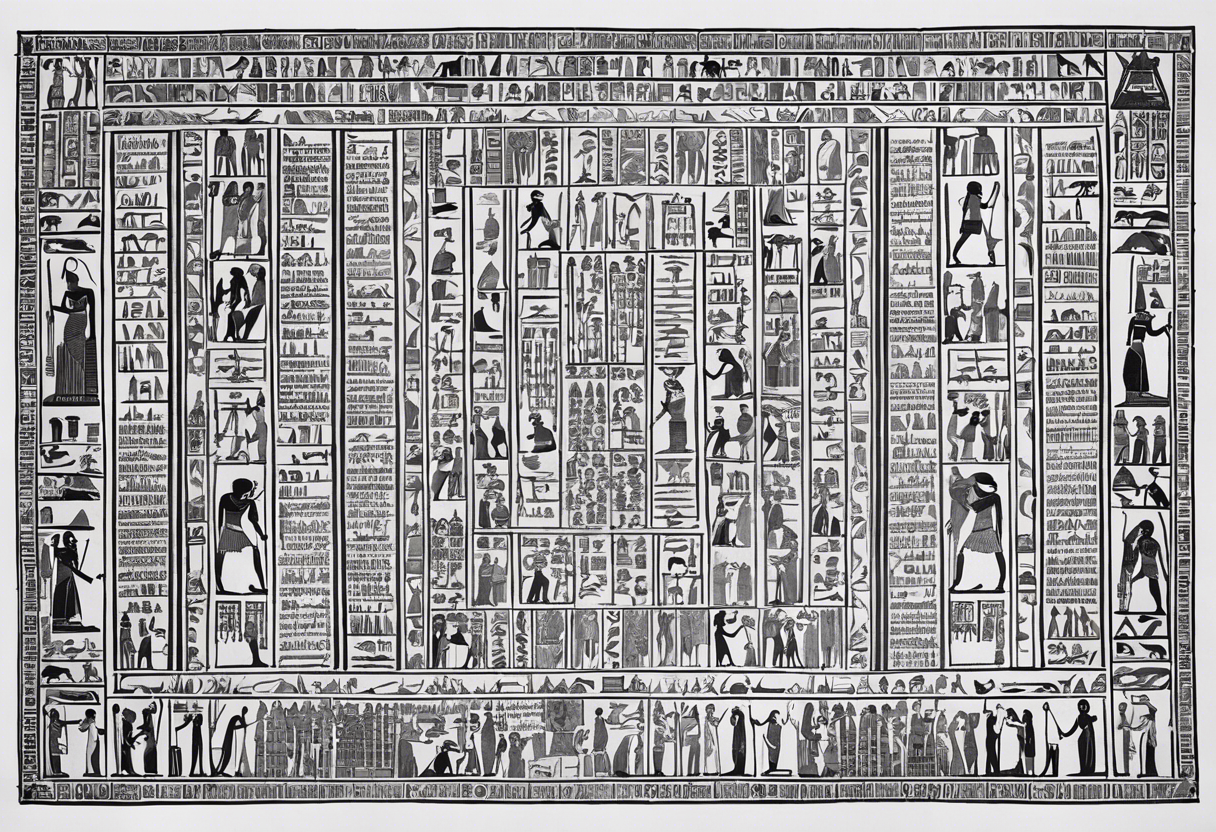
The Book of the Dead is a collection of ancient Egyptian texts that were originally written on papyrus scrolls and placed in tombs as a guide for the deceased in the afterlife. The content of the book varied, but it typically included a combination of spells, prayers, hymns, and rituals. Here is an overview of the main themes and elements found within the Book of the Dead:
The Journey to the Afterlife
One of the primary purposes of the Book of the Dead was to assist the deceased in navigating the treacherous journey to the afterlife. It provided instructions on how to pass through various gates, cross rivers, and pass judgment before the gods. The book also contained maps and guides to help the deceased find their way to the Hall of Ma'at, where their heart would be weighed against the feather of Ma'at, symbolizing truth and justice.
Magical Spells and Incantations
The Book of the Dead contained numerous spells and incantations that were believed to have magical powers and aid the deceased in the afterlife. These spells were meant to provide protection, ensure a successful rebirth, and grant the deceased eternal life. Spells included those to ward off evil spirits, protect against physical harm, and provide nourishment and sustenance in the afterlife.
Offerings and Offeratory Formulae
Another important element found in the Book of the Dead were offerings and offeratory formulae. These were often accompanied by illustrations depicting food, drink, and other goods that were believed to be necessary for the sustenance of the deceased in the afterlife. Offerings were made to the gods and various divine beings in order to gain their favor and assistance.
Rituals and Ceremonies
The book also detailed various rituals and ceremonies that were to be performed by priests or family members on behalf of the deceased. These rituals included the Opening of the Mouth ceremony, which was believed to restore the senses and allow the deceased to speak and eat in the afterlife. Other rituals involved the purification of the body, the anointing of the deceased with oils and perfumes, and the placing of amulets and charms on the body for protection.
Moral and Ethical Instruction
In addition to the practical and magical elements, the Book of the Dead also incorporated teachings on morality and ethics. It emphasized the importance of leading a virtuous life, following Ma'at (truth and justice), and adhering to divine laws. The book stressed the idea that one's actions in life would be judged in the afterlife and that only those who were deemed worthy would be granted eternal life.
The content of the Book of the Dead provides us with valuable insights into the beliefs, rituals, and practices of ancient Egyptian society. It offers a glimpse into their concept of the afterlife and the measures they took to ensure a successful journey and a favorable judgment before the gods.
The Role of the Book of the Dead in Ancient Egyptian Society

The Book of the Dead played a significant role in ancient Egyptian society, as it served as a guidebook for the deceased on their journey through the afterlife. This sacred text, also known as the "Spell for Going Forth by Day", contained spells, prayers, and rituals that were believed to help the deceased overcome obstacles and attain eternal life.
The Importance of the Afterlife
In ancient Egypt, belief in the afterlife was deeply ingrained in society. The Egyptians viewed death as a transitional stage and believed that the soul, or ka, continued its existence in the afterlife. To ensure a successful transition and a favorable afterlife, proper burial rituals and the inclusion of the Book of the Dead were crucial.
Content and Purpose of the Book
The Book of the Dead consisted of a compilation of religious texts and illustrations. It was written on papyri rolls and placed in the tombs of the deceased. The content of the book varied, but it typically included spells, hymns, and instructions for navigating the afterlife. These texts addressed various aspects of the journey, such as judgment, protection from evil spirits, and the safe passage through the underworld.
The primary purpose of the Book of the Dead was to guide the deceased through the perilous journey in the afterlife. The spells and rituals contained within the book were believed to provide protection, aid in judgment, and grant the necessary knowledge and power to overcome challenges encountered in the realm of the dead.
Rituals and Offerings
The Book of the Dead was not only a source of guidance but also played a crucial role in the performance of rituals and the offering of gifts. The rituals performed by the living, such as reciting spells from the book, offering food, beverages, and other items, were believed to provide sustenance and support to the deceased in the afterlife.
Illustrations and Visual Representations
Alongside the textual content, the Book of the Dead was adorned with colorful illustrations depicting scenes from the afterlife and the deceased's journey. These illustrations served as visual aids, helping the deceased understand the rituals and navigate the challenges they would encounter. The images also depicted various gods and mythical creatures, highlighting their importance in the afterlife and emphasizing their involvement in the journey.
Influence on Society
The existence of the Book of the Dead had a profound impact on ancient Egyptian society. It was considered essential for individuals of all social classes to possess a copy of their own or have one provided for their burial. The book was produced by scribes who specialized in its creation, contributing to the professionalization of writing and the development of the scribal class.
Furthermore, the Book of the Dead influenced the art and iconography of ancient Egypt, serving as inspiration for tomb decorations and funerary objects. The religious beliefs and practices associated with the book also shaped the way the Egyptians conceptualized death and the afterlife.
In conclusion, the Book of the Dead held immense significance in ancient Egyptian society. As a guidebook for the deceased, it offered protection, guidance, and spiritual instructions to help individuals navigate the afterlife successfully. It served as a tangible symbol of the Egyptian belief in the continuation of the soul and had a lasting influence on the society's religious practices, rituals, and artistic expressions.
The Afterlife Beliefs of Ancient Egyptians

The ancient Egyptians had a unique and elaborate belief system regarding the afterlife. Their beliefs about the afterlife were deeply rooted in the idea of immortality and the existence of a divine judgment. Understanding their beliefs about the afterlife is crucial to comprehending the significance of the ancient Egyptian Book of the Dead.
The Journey to the Afterlife
Ancient Egyptians believed that after death, the soul would embark on a perilous journey to reach the afterlife. They believed that the deceased person's heart would be weighed against the feather of Ma'at, the goddess of truth and justice. If the heart was found to be free of sin and lighter than the feather, the deceased would be granted eternal life in the afterlife. However, if the heart was heavy with sin, it would be devoured by a fearsome deity called Ammit, resulting in eternal punishment.
The Role of the Book of the Dead
The Book of the Dead was a vital tool in ensuring a successful passage to the afterlife. It was a collection of magical spells and rituals that guided the deceased through the challenges they would face in the afterlife. The spells were believed to provide protection, purification, and resurrection to the soul, allowing it to navigate the treacherous journey and pass the judgment of Ma'at.
Burial Practices and Funerary Rituals
Ancient Egyptians had intricate burial practices designed to preserve the body and provide the deceased with everything they would need in the afterlife. The body was carefully mummified and placed in a tomb filled with items believed to be necessary in the afterlife, such as food, clothing, and personal belongings. Rituals and ceremonies were performed by priests to ensure the proper transitioning of the soul to the afterlife.
Immortality and the Afterlife
The concept of immortality held great significance in ancient Egyptian beliefs about the afterlife. The afterlife was seen as a continuation of life on earth, where the deceased would enjoy the same pleasures and activities they had enjoyed in their earthly existence. The reunion with loved ones and the chance to live eternally in the presence of the gods were highly desirable aspects of the afterlife.
Conclusion
Summary: The ancient Egyptians held unique and intricate beliefs about the afterlife. They believed in a complex journey for the soul, where it would face judgment and either gain eternal life or suffer eternal punishment. The Book of the Dead played a crucial role in guiding the deceased through the challenges of the afterlife. Through elaborate burial practices and funerary rituals, the Egyptians sought to preserve the body and ensure a successful transition to the afterlife. The concept of immortality was central to their beliefs, with the afterlife seen as a continuation of earthly life.
[250 words]
The Illustrations and Texts in the Book of the Dead

The Book of the Dead is renowned for its vivid and intricate illustrations, as well as its rich and detailed texts. These illustrations and texts play a crucial role in guiding the deceased through the afterlife and aiding them in achieving a successful journey.
Illustrations
The illustrations in the Book of the Dead are not merely decorative but contain symbolic meaning and serve as visual aids for the deceased. They depict scenes from the mythological and religious beliefs of ancient Egypt, as well as portray the rituals and ceremonies associated with death and the afterlife.
One prominent illustration found in many versions of the Book of the Dead is the weighing of the heart ceremony. This scene shows the deceased standing before an ornate scale, with the god Osiris presiding over the judgment. The heart of the deceased is weighed against the feather of Ma'at, the goddess of truth and justice. If the heart is found to be pure and free from wrongdoing, the deceased is granted eternal life. These illustrations provide a tangible representation of the moral and ethical expectations of Egyptian society.
Another common illustration found in the Book of the Dead is the journey of the sun god Ra through the underworld during the nighttime hours. This complex and detailed depiction showcases the various obstacles and challenges the deceased must overcome to join Ra in his daily rebirth, ensuring their own resurrection and continued existence in the afterlife.
Texts
Accompanying these illustrations are detailed texts that provide instructions, prayers, and incantations for the deceased. These texts are written in hieroglyphics, the ancient Egyptian writing system comprising symbols and pictograms.
The texts in the Book of the Dead serve several functions. They act as guidebooks, directing the deceased on their journey and advising them on the correct rituals and actions to perform. They include spells and incantations intended to protect the deceased from harm, ward off evil spirits, and facilitate their transformation into a divine being.
One particularly important text often included in the Book of the Dead is the Negative Confession or the Declaration of Innocence. This series of declarations allows the deceased to assert their innocence and proclaim that they have not committed specific sins or violated moral codes. By reciting these declarations, the deceased can prove their worthiness to judges and deities in the afterlife.
Overall, the illustrations and texts in the Book of the Dead work in harmony to provide a comprehensive guide for the deceased on their journey through the afterlife. They combine imagery and words to convey the necessary knowledge and rituals required to attain a favorable outcome in the afterlife. Through the careful study of these illustrations and texts, we gain insights into the religious beliefs, cultural values, and the aspirations of the ancient Egyptians regarding the afterlife.
The Spells and Rituals in the Book of the Dead

The Book of the Dead is a collection of religious and magical spells that were meant to guide the souls of the dead through the afterlife. These spells and rituals were believed to provide the deceased with the necessary tools and knowledge to navigate the perilous journey to the afterlife and ensure their ultimate salvation.
A Guide to the Afterlife
One of the main purposes of the Book of the Dead was to provide a comprehensive guide to the afterlife. The spells and rituals contained in the book were intended to help the deceased understand the journey they would undertake and the challenges they would face along the way. These rituals offered prayers, invocations, and magical incantations to secure the assistance of various gods and goddesses and to gain their favor in the afterlife.
Protection and Transformation
Many of the spells in the Book of the Dead focused on providing protection and transformation to the deceased. The ancient Egyptians believed that the afterlife was fraught with dangers, and it was essential for the deceased to be able to defend themselves against these threats. Spells such as the "Book of Going Forth by Day" offered protection against evil spirits and ensured the safety of the deceased during their journey.
Invocation of Deities
A significant aspect of the Book of the Dead was the invocation of various deities. The spells and rituals called upon gods and goddesses such as Osiris, the god of the dead, and Anubis, the god of embalming and mummification, to assist the deceased in their journey. These invocations sought the favor and protection of these powerful beings, in exchange for offerings and praise.
Rituals for Judgment
Another significant component of the Book of the Dead were the rituals related to judgment in the afterlife. The ancient Egyptians believed that after death, the deceased would face a judgment by the god Osiris. Spells such as the "Declaration of Innocence" were recited to prove the worthiness of the deceased and ensure a favorable judgment. These rituals offered the deceased a chance to state their case and demonstrate their righteousness.
Transformation into an Akh
One of the ultimate goals of the spells and rituals in the Book of the Dead was the transformation of the deceased into an akh, a blessed and glorified spirit. The rituals provided guidance on how to navigate the challenges of the afterlife successfully and gain ultimate rebirth. Through the recitation of spells and the performance of rituals, the deceased sought to achieve this transformation and become a divine being in the afterlife.
In conclusion, the spells and rituals in the Book of the Dead served as a guide to the afterlife, offering protection, invoking deities, facilitating judgment, and enabling transformation. By following the instructions outlined in this ancient text, the deceased believed they could navigate the challenges of the afterlife and ultimately achieve eternal salvation.
The Legacy of the Book of the Dead

The Ancient Egyptian Book of the Dead holds a profound legacy that continues to captivate scholars and the general public alike. Its impact can be observed in various aspects, including its influence on art, religion, and our understanding of ancient Egyptian civilization.
Artistic Inspiration
One of the remarkable legacies of the Book of the Dead is its influence on ancient Egyptian art. The vibrant illustrations and hieroglyphic texts featured in the papyrus scrolls have served as a rich source of inspiration for artists throughout history. The intricate details and symbolic depictions found in the Book of the Dead have been emulated and reinterpreted in various art forms, providing a glimpse into the beliefs and traditions of ancient Egypt.
Spiritual Significance
The Book of the Dead reflects the religious beliefs and practices of the ancient Egyptians concerning the afterlife. It was created to guide and assist the deceased in their journey through the underworld, providing them with spells, incantations, and instructions necessary for a successful transition into the afterlife. This spiritual significance is not only limited to ancient times but continues to resonate with individuals interested in exploring and understanding the mysteries of the afterlife.
Insight into Ancient Egyptian Civilization
The Book of the Dead is a valuable historical document that offers significant insights into the beliefs, customs, and societal norms of ancient Egypt. It provides us with a comprehensive understanding of the complex rituals and religious practices associated with death and the afterlife. Through its intricate illustrations and detailed texts, we gain a deeper appreciation for the hierarchical structure of ancient Egyptian society, the role of priests, and the importance of ensuring a proper burial for a successful journey to the afterlife.
Influence on Egyptology
The study of the Book of the Dead has played a crucial role in the field of Egyptology. Scholars and archaeologists have relied on this ancient text to decipher ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics and decode the language of the period. The meticulous translations and analysis of the Book of the Dead have significantly contributed to our understanding of the ancient Egyptian language, culture, and religious practices. It acts as a cornerstone for the field of Egyptology, guiding researchers in their quest to unravel the mysteries of this fascinating civilization.
In conclusion, the Book of the Dead is not simply a historical artifact but a testament to the rich cultural and spiritual legacy of ancient Egypt. Its influence on art, religion, and our understanding of ancient Egyptian civilization is undeniable. As we continue to explore and interpret this ancient text, we uncover new insights into the beliefs, rituals, and traditions of one of the most enigmatic civilizations in human history.
Comparisons with Other Funerary Texts

The Ancient Egyptian Book of the Dead is a unique and unparalleled text in its exploration of the afterlife. However, it is not the only funerary text that existed in ancient Egypt. There are several other texts that provide insights into the beliefs and rituals surrounding death and the journey to the afterlife. Comparisons between these texts can shed light on the similarities and differences in the ancient Egyptian understanding of the afterlife.
The Pyramid Texts
One of the oldest funerary texts in ancient Egypt is the Pyramid Texts, dating back to the Old Kingdom (c. 2686-2181 BCE). These texts were exclusively inscribed on the walls of royal pyramids and were meant to guide the deceased pharaohs in the afterlife.
Unlike the Book of the Dead, the Pyramid Texts primarily focus on the divine transformation and deification of the pharaoh. They contain spells and rituals that aimed to ensure the pharaoh's successful transition to the realm of the gods.
The Coffin Texts
The Coffin Texts, which emerged during the Middle Kingdom (c. 2055-1650 BCE), were similar to the Pyramid Texts but were more accessible to a broader range of people. The rituals and spells in the Coffin Texts were inscribed on wooden coffins, providing a more widespread access to the afterlife beliefs.
While both the Book of the Dead and the Coffin Texts share some common themes and spells, the latter includes a broader array of texts that vary depending on the individual's social status and personal beliefs.
The Book of Caverns and Amduat
The Book of Caverns and the Amduat are two funerary texts that focus on the journey of the sun god through the underworld during the nighttime hours. Unlike the Book of the Dead, these texts present a more narrative-driven account of the afterlife journey.
The Book of Caverns, found in the tombs of the New Kingdom (c.1550-1070 BCE), illustrates the sun god Ra's journey through twelve caves, each representing different regions of the underworld. The Amduat, on the other hand, follows the sun god on his journey across twelve nocturnal hours, battling various serpents and other creatures of darkness.
Similarities and Differences
While the Book of the Dead, Pyramid Texts, Coffin Texts, Book of Caverns, and Amduat each offer insights into the ancient Egyptian beliefs about the afterlife, they differ in their content, purpose, and intended audience.
The Book of the Dead, compared to the Pyramid Texts, is more focused on providing instructions and spells for the deceased to navigate the complex challenges encountered in the afterlife. In contrast, the Pyramid Texts emphasize the deification of the pharaoh rather than the individual's journey.
The Coffin Texts, while sharing some similarities with the Book of the Dead, incorporate a broader spectrum of texts and rituals tailored to individual preferences. Moreover, the Book of Caverns and the Amduat offer more narrative-driven accounts of the afterlife journey, providing vivid descriptions of the challenges and obstacles faced by the sun god.
Overall, the various funerary texts of ancient Egypt collectively offer a comprehensive understanding of the afterlife beliefs and rituals. The Book of the Dead stands out as a distinct text for its detailed instructions and spells, while the other texts provide complementary insights into different aspects of the ancient Egyptian journey to the afterlife.
Modern Understanding and Interpretation of the Book of the Dead

The Book of the Dead, an ancient Egyptian funerary text, has fascinated scholars and researchers for centuries. Over time, our understanding and interpretation of this ancient manuscript have evolved as we uncover more knowledge about ancient Egyptian culture, religion, and language.
- Deciphering the Hieroglyphs
One of the significant challenges in understanding the Book of the Dead was deciphering the hieroglyphs in which it was written. During the early days of Egyptology, scholars struggled to make sense of the complex symbols and translate the text accurately. However, advancements in linguistic analysis and the translation of the Rosetta Stone by Jean-François Champollion in 1822 provided a crucial breakthrough. This allowed researchers to decipher the hieroglyphs and comprehend the content of the Book of the Dead with greater accuracy.
- Religious and Mythological Interpretations
The Book of the Dead serves as a guide for the deceased's journey through the afterlife. It contains spells, incantations, and illustrations that were intended to assist and protect the deceased in various stages of their journey. Modern scholars have studied the religious and mythological aspects of the text to gain a deeper understanding of the beliefs and practices of ancient Egyptians.
Some interpret the book as a reflection of the Osirian belief system, which centers around the god Osiris. They view the journey described in the Book of the Dead as paralleling Osiris' own journey through death and resurrection. Others emphasize the symbolic nature of the text, seeing it as an allegorical representation of the deceased's spiritual transformation.
- Role of Ritual and Magic
The Book of the Dead also offers insights into the role of ritual and magic in ancient Egyptian religious practices. The spells and incantations found in the text were believed to have the power to protect the deceased from harm and ensure their successful journey into the afterlife. Researchers have examined these rituals, spells, and amulets mentioned in the text to better understand the religious practices of the time.
It is important to note that modern interpretations of the Book of the Dead are speculative to some extent due to the limited information available and the variations found in different versions of the text. However, by analyzing the text in conjunction with other ancient Egyptian religious texts, inscriptions, and archaeological evidence, scholars have made significant progress in reconstructing the beliefs and practices associated with the book.
- Cultural and Historical Significance
The Book of the Dead holds immense cultural and historical significance. It provides us with valuable insights into the beliefs, rituals, and worldview of ancient Egypt. Through the text, we can gain a better understanding of their understanding of death, the afterlife, and the role of individuals in the divine order.
Furthermore, the Book of the Dead showcases the highly elaborate and meticulous preparations Egyptians made for the afterlife, including the preservation of the body, the construction of elaborate tombs, and the inclusion of personal belongings and important texts like the Book of the Dead.
In conclusion, while our understanding and interpretation of the Book of the Dead have evolved over time, it remains a vital source of information about ancient Egyptian funerary practices, religious beliefs, and mythology. Through ongoing research and analysis, scholars continue to delve deeper into the complexities of this ancient text, shedding light on the rich and fascinating culture of ancient Egypt.

إرسال تعليق